Pneumonia caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most dangerous infections that can occur in hospital. Particularly worrying are multi-resistant strains, against which many antibiotics are no longer effective. These pathogens are widespread worldwide and pose a major challenge even for modern healthcare systems. Despite intensive therapy, mortality among affected patients is over 20 percent.
“Even with effective antibiotics, infections with Staphylococcus aureus are often difficult to treat,” says Prof. Mark Brönstrup, senior author of the study and head of the ‘Chemical Biology’ department at the HZI. “Our novel strategy therefore does not attack the bacterium itself, but specifically neutralizes a toxin it produces. This opens up a new therapeutic perspective – especially for critically ill people at high risk.”
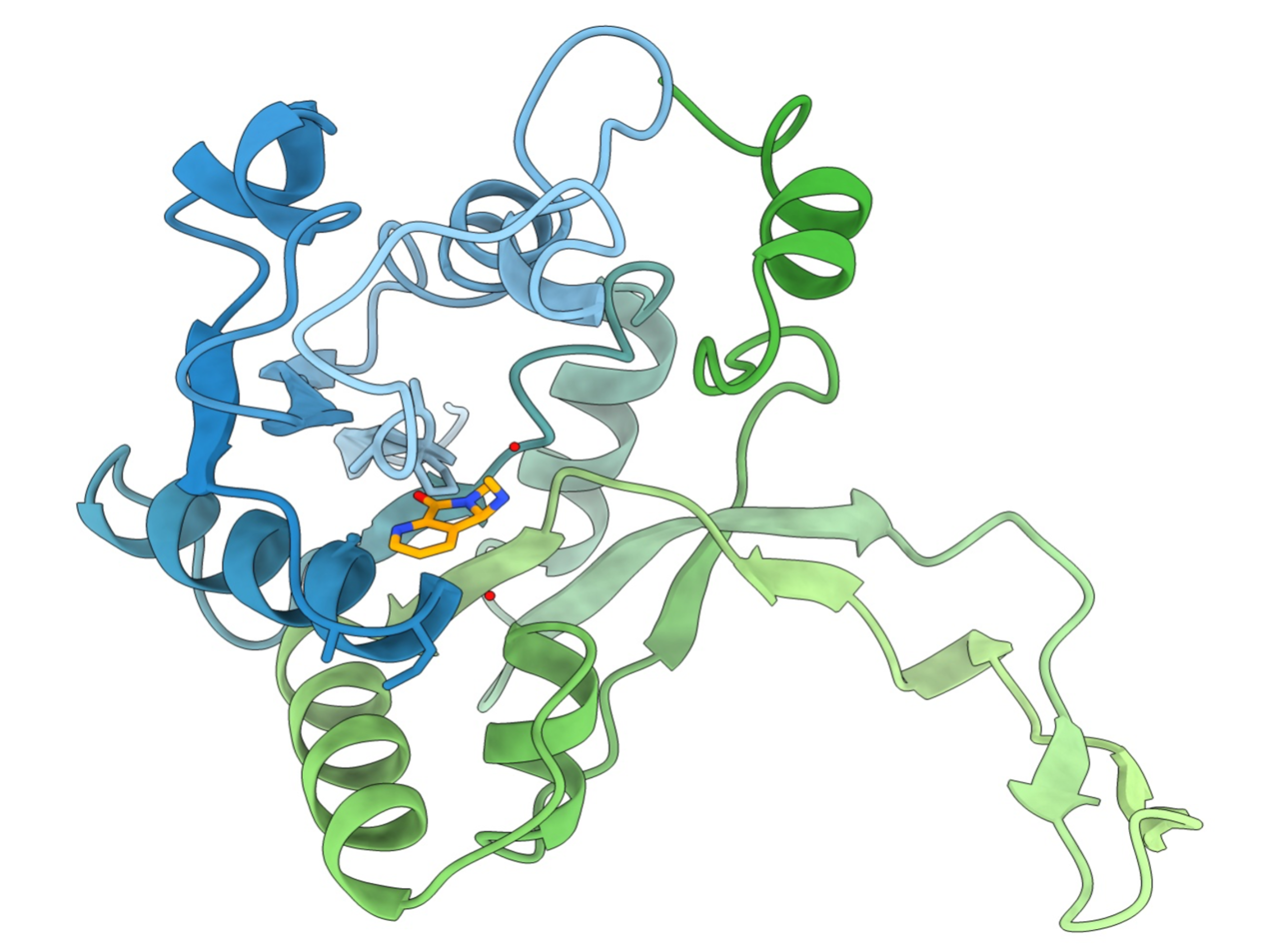
The new research approach is aimed at the targeted inhibition of the key virulence factor α-hemolysin. Hemolysin is a protein that forms pores in cell membranes in the lungs, leading to the destruction of lung tissue and immune cells, inflammation and ultimately to a worsening of the disease. The researchers developed a miniaturized test system that allowed them to screen over 180,000 compounds for their ability to block the effect of α-hemolysin. Drug candidates from the quinoxalinedione class, in particular the compound H052, proved to be highly effective, both in cell culture and in animal models.
“Our goal was to develop a small molecule that neutralizes the toxin before it causes damage – and that is exactly what the quinoxalindiones do,” says Dr. Aditya Shekhar, first author of the study. ”It was particularly impressive that we were not only able to protect cells, but also significantly improve survival in infected mice.”
In the mouse model, the active substance was able to increase the survival rate in the case of an acute lung infection with the highly virulent S. aureus USA300 strain, both when administered preventively or therapeutically. At the same time, inflammatory markers and the bacterial load in the lungs of immunocompetent mice were reduced. The combination of H052 with the antibiotic linezolid was also effective.
New approaches in the fight against antibiotic resistance
The concept of so-called “pathoblockers”, i.e. agents that target bacterial virulence mechanisms rather than the bacterium itself, is considered a promising approach. Since no selective pressure is exerted on the bacterium, the risk of development of resistance is significantly lower.
“Our results show that even large bacterial toxins can be specifically inhibited by small molecules – this opens doors for a completely new class of anti-infectives,” adds Shekhar. Thanks to good manufacturing options and tolerability, the drug candidate H052 could be used in particular as an infusion preparation in hospitals – for example to prevent severe pneumonia in high-risk patients.
The research was carried out mainly at the HZI in Braunschweig and as part of the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF) in close partnership with the Lead Discovery Center (LDC) in Dortmund. The research team received milestone-dependent funding of 4,9 million US dollars to date from the non-profit organization Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator (CARB-X); CARB-X has indicated that further funding may be provided through the end of Phase 1 of the clinical trial based on project progress.
Background: Responsible approach to animal testing
The animal experiments with mice used in this study were carried out in strict compliance with the applicable legal requirements and ethical standards. The aim was to generate meaningful data with as few animals as possible that could contribute to the development of new therapeutic options for seriously ill patients. The insights gained represent an important step towards developing animal-free models and clinical applications in the long term.